These days most engineers understand the benefits of migrating to IP networks for audio and video transport. However, we still field quite a few questions about AMWA NMOS and how this protocol can be used to manage AES67, ST 2110-30 and ST 2022-7 IP streams. So we thought it might be useful to expand a little on the benefits of NMOS.
The Elements of NMOS (Networked Media Open Specifications)
NMOS is a set of open standards developed by the Advanced Media Workflow Association (AMWA). Tieline codecs support NMOS IS-04 (Discovery and Registration) and IS-05 (Connection Management), supporting interoperability, discovery, connection management, and control in IP-based networks.
Benefits of NMOS
AMWA states that:
NMOS is the open-source “special sauce” that enables connection, management, and control of your IP video and audio devices from different manufacturers – in a common eco-system and in an interoperable way.
More specifically, the benefits of NMOS include:
- Devices from a variety of vendors can work together
- API-driven control of audio stream routing is provided across a network
- Smarter integration with IP consoles, routers, and other devices without requiring custom wiring or coding
- Scalable as your network grows as it is simple to add devices and streams and configure them
This allows you to build a network with equipment tailored to your specific needs and requirements.
IS-04 and IS-05: Discovery, Registration and Control
Discovery and Registration allows components within a networked media system to find each other. NMOS also provides connection management. This is required because essential components for controlling and managing network devices are not included in the SMPTE standards, e.g. AES67 and ST 2110.
NMOS delivers specifications in the form of APIs. In a network supporting NMOS, each node exposes one or more NMOS APIs in order to find, register and control resources on each node. For example, in a Tieline Gateway codec we can access the NMOS API by entering the AoIP port (e.g. AoIP 1) IP address and NMOS port in a browser, e.g. 192.168.87.80:8081. It displays as follows:
NMOS: Practical Applications for Codec Users
A Tieline codec with NMOS enabled on source and destination IP streams can:
- Register itself via IS-04
- Be connected via IS-05
IS-05 also facilitates seamless switching to a backup AoIP stream using ST 2022-7, which defines the method for hitless packet switching over IP. Tieline’s next major firmware release will support this too.
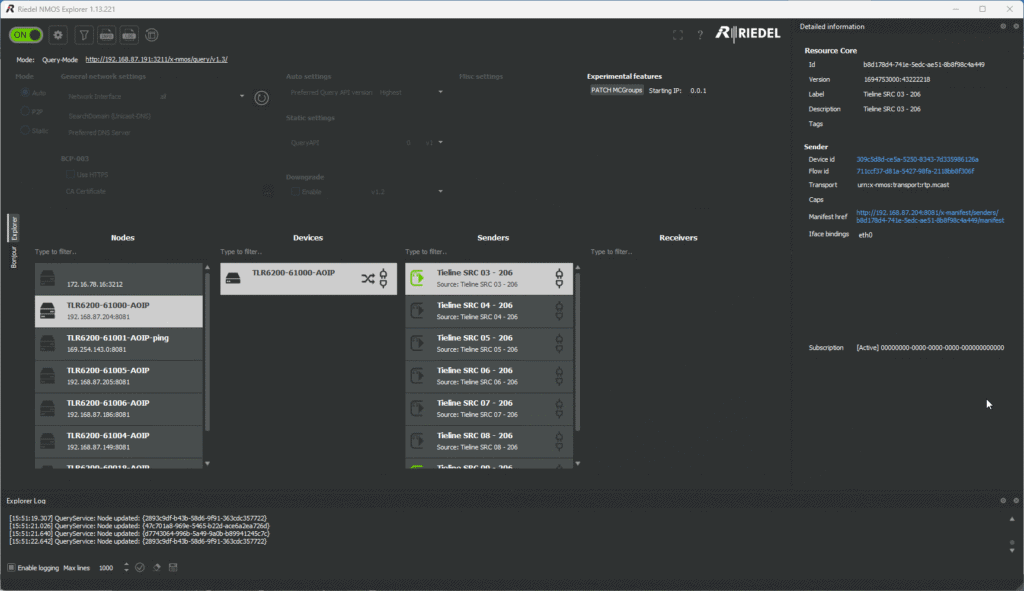
An NMOS server in a codec can integrate with software tools such as Riedel NMOS Explorer, which can discover, manage and connect IP Media Devices following IS-04 and IS-05 standards. Some of the options that are supported in Tieline codecs include:
- Discovery of nodes, devices and streams
- The ability to view and configure stream parameters – including displaying and copying SDP
- Starting and stopping streams.

IS-07: Event and Tally
The IS-07 NMOS specification provides a mechanism for facilitating signal exchanges (transmit and receive) for state changes, GPIOs, tally and other triggered events. It allows the use of logic IOs instead of physical GPIOs, which provides greater flexibility and scalability. Tieline will support this in an upcoming firmware release.
The Future of NMOS
NMOS will continue to develop over time to provide smarter, more flexible, and more secure IP networks for broadcasters. More information, including videos and white papers, is available at https://www.amwa.tv/